

All those costs which are not charged against the income of the period are carried forward. Under accounting by the accrual basis, the costs are matched either against revenues or against the relevant time period in order to determine the net income. What is Accrued ExpensesĪccrued expenses refer to an expense related to the business operation which is recognized in the books of the accounts before it is paid, and these expenses are recorded in the books for the period they are actually incurred. Thusly, it would help if you focused on the statement of incomes of a business, which demonstrates the cash flow in and out of business. The outcome can be an apparently beneficial element that is starved for money, and which may go bankrupt despite its accounted for level of profit. One of the disadvantages of the accrual basis of accounting is that it can depict the presence of profits, despite the fact that the related capital inflows have not happened yet. Problems with the Accrual Basis of Accounting This can result in the deferral of IT payments. Likewise, a business owner might decide to control the timing of capital inflows and surges to create a smaller measure of taxable income under the cash basis of accounting. When to Avoid the Accrual Basis of Accounting?Ī small business might choose to abstain from utilizing the accrual basis of accounting, since it requires a specific measure of expertise. So any cost thereafter which appears to have lost its utility or its power to generate future revenue is written-off as a loss.

Expenses that are not loaded to the income statement or profit and loss statement are carried forward and are kept under continuous review.Expenses or costs are matched either against revenues so recognized or against the relevant time period to determine periodic income.The essential features of the accrual basis of accounting are: It also recognizes the assets, liabilities, revenue and accrued expenses for the amounts received or paid in cash in the past, and amounts expected to be paid or received in cash in the future. The motive behind following the accrual basis of accounting is to relate the accomplishments (measured in the form of revenue ) and the efforts (measured in terms of cost ) so that reported income ( net of expenses ) measures an enterprise’s performance during a period instead of merely listing its cash receipts and payments. The accrual basis of accounting recognizes that buying, producing, selling and other economic events that affect the enterprise’s performance often do not coincide with the cash receipts and payments for the given period. How Does Accrual Basis of Accounting Works?Īccrual basis of accounting tries to record the financial effects of the transactions, events, and circumstances of an enterprise in the period in which they occur rather than recording them in the time period in which cash is received or paid by the enterprise. This basis of accounting is also referred to as ‘Mercantile Basis of Accounting’. This includes considerations relating to deferrals, allocations, depreciation and amortization. The procedure of recording transactions by which revenue, cost, assets and liabilities are reflected in the accounts for the period to which they accrue. The word “Accrual” can be explained as revenue and cost are accrued i.e., they are recognized as earned or incurred (irrespective of whether money is received or paid) and entered in the books of accounts for the period to which they relate. The following are three accounting foundations that are used by the business. One of the fundamental accounting assumptions associated with the preparation and presentation of financial statements is the accrual basis of accounting. Differences Between Accrual Basis of Accounting and Cash Accounting.Examples of Accrual Basis of Accounting and Accrued Expenses.Features of Accrual Basis of Accounting.
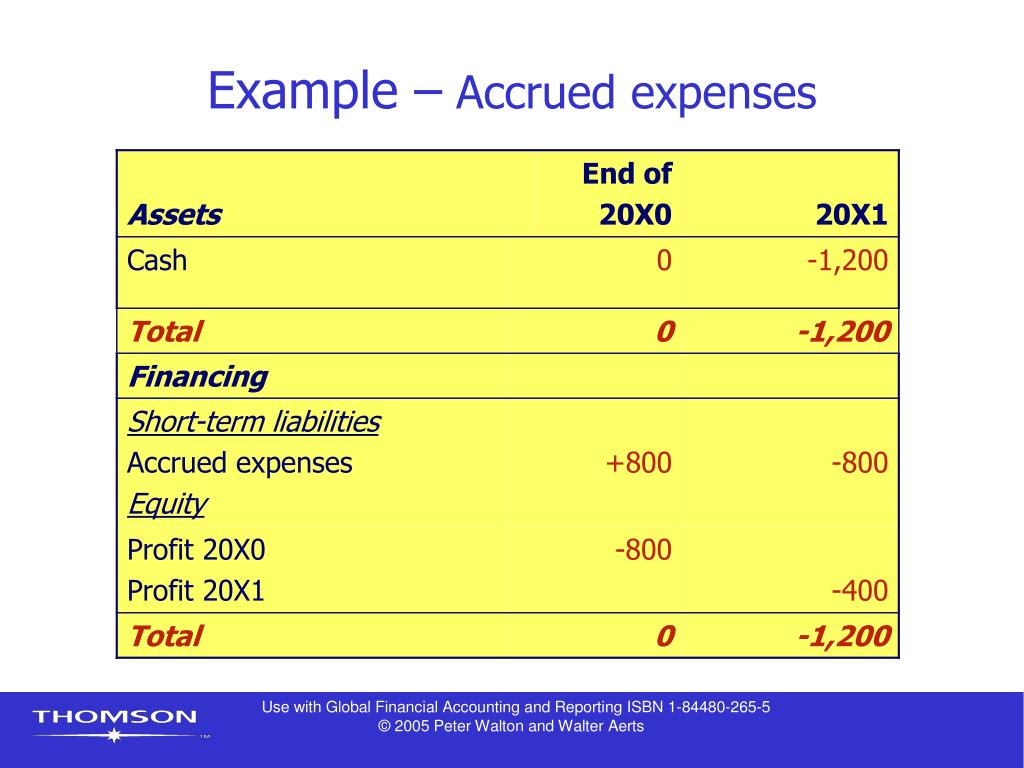
How Does Accrual Basis of Accounting Works?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
